AndroidSecurityTraining
Tags:
Learn Android security through hands-on labs with parallel secure and vulnerable implementations for each topic. This project covers 10 key security areas, each provided in two flavors: a best-practice secure build and a deliberately vulnerable build to illustrate common pitfalls.
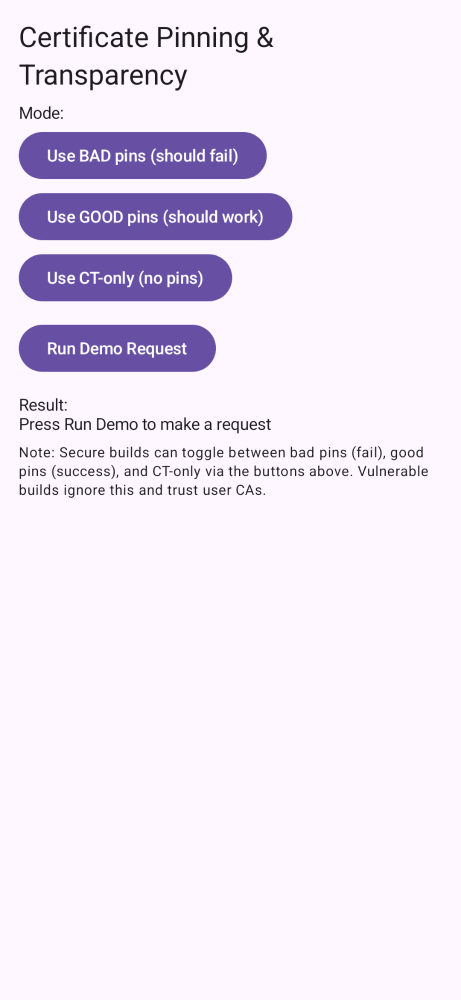

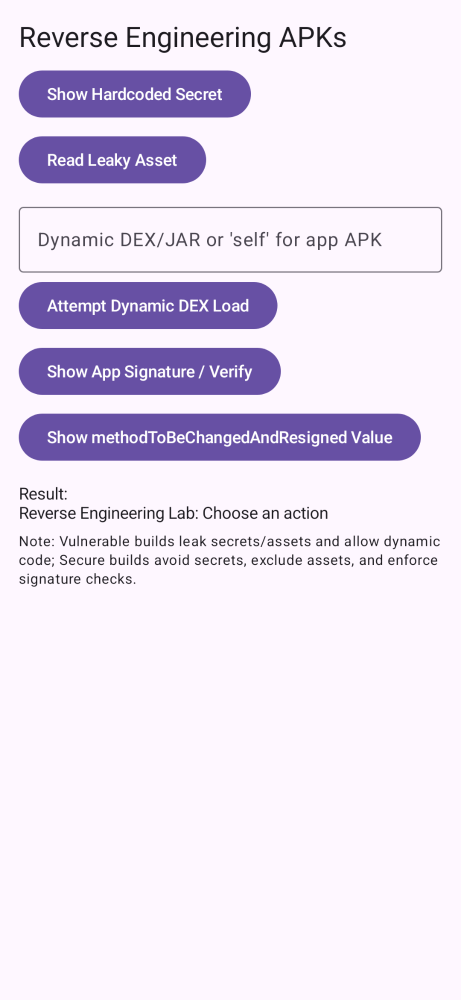
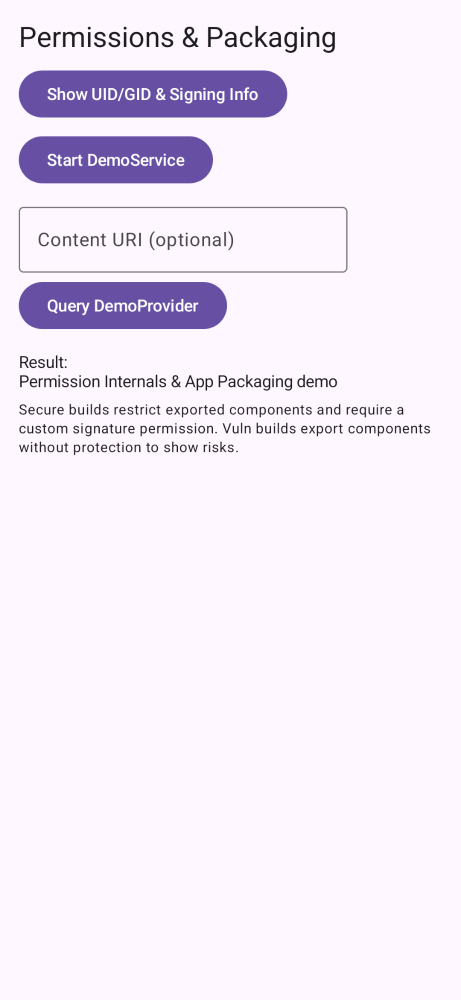
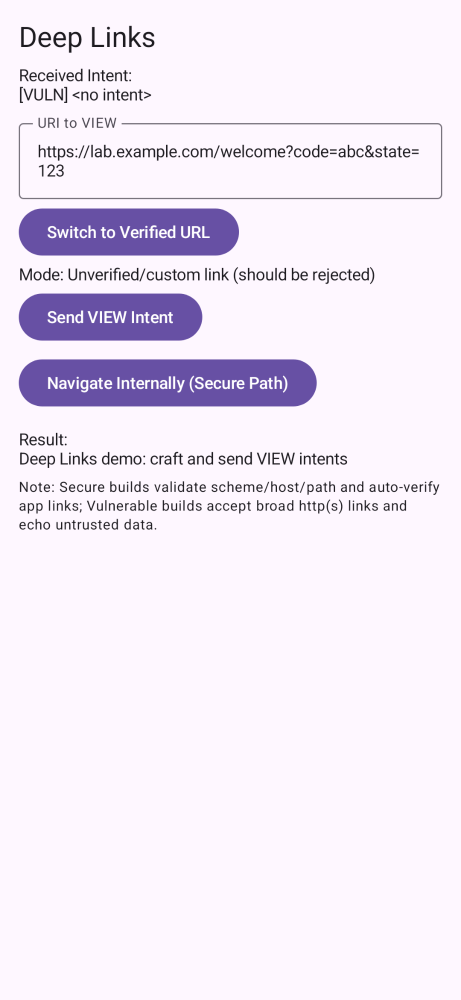


Table of contents
- Purpose and scope
- Prerequisites (tools) and before‑you‑start
- Quick start
- Build variants (how this project is organized)
- Topics: how to run the labs (index)
- MITM proxy quick setup (mitmproxy + emulator)
- Getting a rooted emulator
- Frida
- Troubleshooting
Purpose and scope
- Goal: Help Android developers learn modern security practices through code you can run, inspect, and modify.
- How: Build one topic at a time and toggle secure vs. vulnerable behavior. Use a proxy or other tools to observe differences.
- Outcome: Understand why attacks work against the vulnerable build and how the secure build stops them.
Prerequisites (tools) and before‑you‑start steps
- Android Studio (latest stable) with Android SDK and emulator images installed.
- Java 21 toolchain (Gradle wrapper config uses JDK 21 compatibility).
- A device or emulator. For interception/root labs, prefer an emulator you control (see rooted emulator section).
- Optional but recommended for labs:
- mitmproxy, Burp Suite, or OWASP ZAP
- Wireshark or tcpdump
- jadx, jadx‐gui and apktool installed
- DB Browser for SQLite (to inspect pulled SQLite .db files) https://sqlitebrowser.org/
- (optional) Frida
- sqlite3 CLI (alternative) — download from https://www.sqlite.org/download.html
- Before you start:
- Clone this repo and open it in Android Studio.
- Let Gradle sync and index completely.
- Decide which topic you want to run first (see Build variants), then pick a secure or vuln profile.
- If you plan to demo MITM, configure your proxy and device/emulator networking first.
Quick start
- Open the project in Android Studio (latest stable).
- In Build Variants, choose a pair like
vulnPinning(to see the issue) thensecurePinning(to see the fix). - Run on an emulator or device and follow the on‑screen actions for the selected topic.
- For network labs, configure your proxy before launching the vulnerable build.
Build variants (how this project is organized)
- Two flavor dimensions in
app/build.gradle.kts:- securityProfile:
secure(best practices) orvuln(intentionally unsafe). Release builds are disabled forvuln. - topic:
pinning,e2e,re,perm,links,storage,root,web,users,risks.
- securityProfile:
- The final build variant is
<securityProfile><Topic>, for example:securePinning,vulnPinningsecureWeb,vulnWeb, etc.
- Routing is handled by per‑flavor providers so the right helper is compiled for each variant.
Troubleshooting
- Build with the Gradle wrapper from Android Studio. If secure pinning fails, check device time and that pins match the current server keys.
- Deep links require a matching
assetlinks.jsonon your domain. Update host/path if you change it. - For MITM demos, remember: secure flavors do not trust user CAs; use vuln flavors.
- If the emulator won’t run as root, confirm you didn’t pick a Google Play image (see section above).
- Expect‑CT (legacy): https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/Headers/Expect-CT
